A Multi-Objective Optimization Approach for Secure MPC in Cloud Environments
Abstract
Cloud computing has transformed the deployment of Machine Learning (ML) applications, yet privacy and security challenges persist when processing sensitive data. Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC) protocols like SPDZ address these concerns but introduce computational overhead, particularly for matrix multiplication (MM) operations essential to deep learning (DL). This work optimizes secure MM performance over MPC by strategically allocating computational resources across Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and Virtual Machines (VMs) with varying attack probabilities. We formulate this as a Multi-Objective Optimization Problem (MOOP) that aims to minimize execution time and cost, where cost includes both computational expenses and potential liability from data breaches while reducing the risk of privacy violations. Using Game Theory methods and Pareto optimality, we develop three approaches: the first optimize execution time, the second prioritizes privacy, and the third balances both objectives. Our comprehensive evaluation proposes a deployment architecture for multiple cloud providers, compares allocation strategies under different VM and VPC distinguishability scenarios, and examines the impact of Strassen’s algorithm depth on performance-security tradeoffs. Implementation in the MP-SPDZ framework demonstrates that our approach significantly improves execution efficiency while maintaining strong privacy guarantees for sensitive ML workloads.
Key Contributions
This work makes three significant contributions to the field of secure multiparty computation:
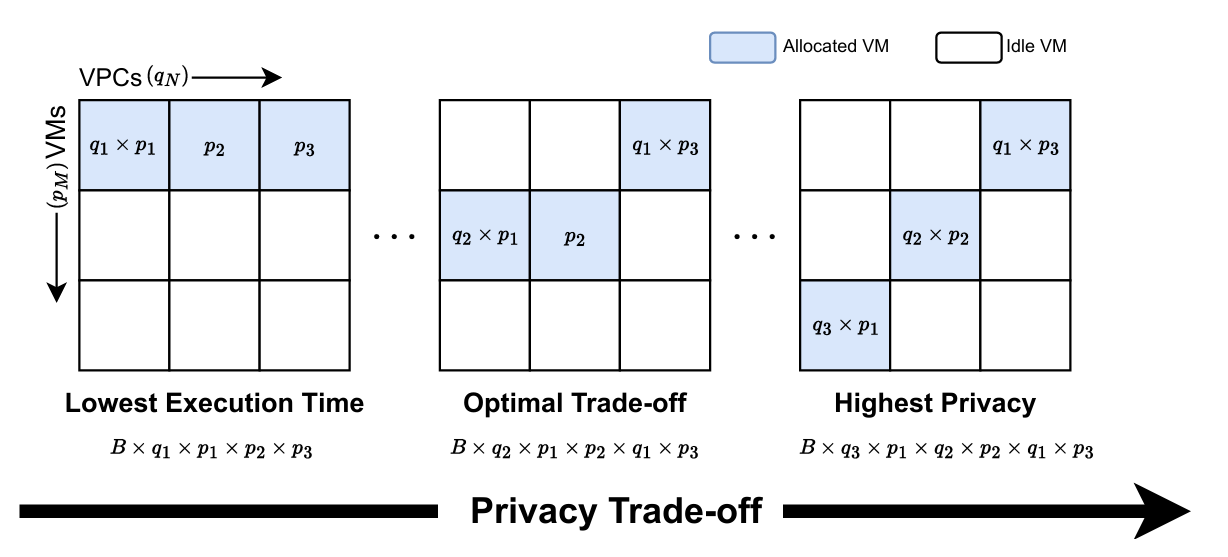
Multi-Objective Formulation
We model the allocation of VMs across VPCs with distinct attack probabilities as a MOOP aiming to minimize execution time and cost while assuring privacy. This approach addresses the inherent trade-offs between performance and security in cloud-based MPC deployments.
Enhanced MM Performance over MPC
We introduce a strategic resource allocation scheme that leverages Strassen’s algorithm to reduce computational overhead and improve MM performance in protocols like SPDZ. Our approach considers the impact of different recursion depths on the performance-security balance.
Game-Theoretic and Pareto Approaches
We solve the MOOP using Nash equilibrium concepts and Pareto optimality, developing allocation strategies that balance performance and security trade-offs for efficient and secure ML/DL workflows. Our three complementary approaches cover different optimization priorities from highest privacy to lowest execution time.
Research Impact
This research addresses critical challenges in privacy-preserving machine learning by providing practical frameworks for deploying MPC protocols in multi-cloud environments. The work demonstrates how strategic resource allocation can significantly enhance both security and performance, making privacy-preserving computation more viable for real-world applications in healthcare, finance, and government sectors.
The integration of game theory with multi-objective optimization provides a novel approach to balancing competing objectives in secure computation, while the comprehensive evaluation across different VM and VPC configurations offers practical guidance for system deployment.
Publication Details
- Venue: -
- Status: Approved for Public Release (Case Number: AFRL-2025-2204)
- Collaboration: Florida International University & Air Force Research Laboratory
- Distribution: Unlimited
This work was supported by the AFRL/RI Internship Program for Summer 2023, representing a successful collaboration between academic research and military applications of secure computation technologies.